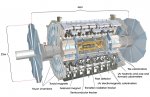
The ATLAS (A Toroidal LHC ApparatuS) experiment is the largest of four detectors in the LHC (Large Hadron Collider) at CERN, located 100m underground and designed to take advantage of the unprecedented energy available at the LHC.
Thousands of particles, produced during the collisions in the center of ATLAS pass through a succession of devices, to determine their properties:
![]() The tracker is a cylinder five meters long and one meter in diameter. Made up of very precise sensors, it can locate charged particles and measure their momentum.
The tracker is a cylinder five meters long and one meter in diameter. Made up of very precise sensors, it can locate charged particles and measure their momentum.
![]() The calorimeter is destructive: it stops all the particles that hit it with the exception of muons, neutrinos, and perhaps unknown weakly interacting particles. Thanks to its fine segmentation, the calorimeter measures the energy and the position of the particles. The calorimeter is an airtight cylinder ten meters long and five meters in diameter.
The calorimeter is destructive: it stops all the particles that hit it with the exception of muons, neutrinos, and perhaps unknown weakly interacting particles. Thanks to its fine segmentation, the calorimeter measures the energy and the position of the particles. The calorimeter is an airtight cylinder ten meters long and five meters in diameter.
![]() The muon spectrometer surrounds the calorimeter and identifies the muons which have passed through the entire detector. The two trackers of the muon system are immersed in a magnetic field which bends the trajectory of the charged particles: to allow precise determination of their momentum.
The muon spectrometer surrounds the calorimeter and identifies the muons which have passed through the entire detector. The two trackers of the muon system are immersed in a magnetic field which bends the trajectory of the charged particles: to allow precise determination of their momentum.
The electrical signals left by the particles that have interacted in each of these devices are routed outside the ATLAS cavern through optical fibers. These signals are then processed by electronic and computer systems and then transmitted through high-speed networks to the computing grid.
LAPP engineers and technicians have built portions of the ATLAS liquid argon calorimeter, as well as parts of its readout electronics, and currently assure stable real-time processing of the calorimeter data. For Run 3 of the LHC the LAPP group delivered new electronic boards (LATOME) for the liquid Argon calorimeter which provide ten-fold improvement for the granularity of the calorimetric triggers. The LAPP is also participating in the construction of a new tracker (ITK) and the replacement of electronic boards providing the calibration and the TTC for the liquid argon calorimeter, for Phase 2 of the detector upgrades (2026-2028).